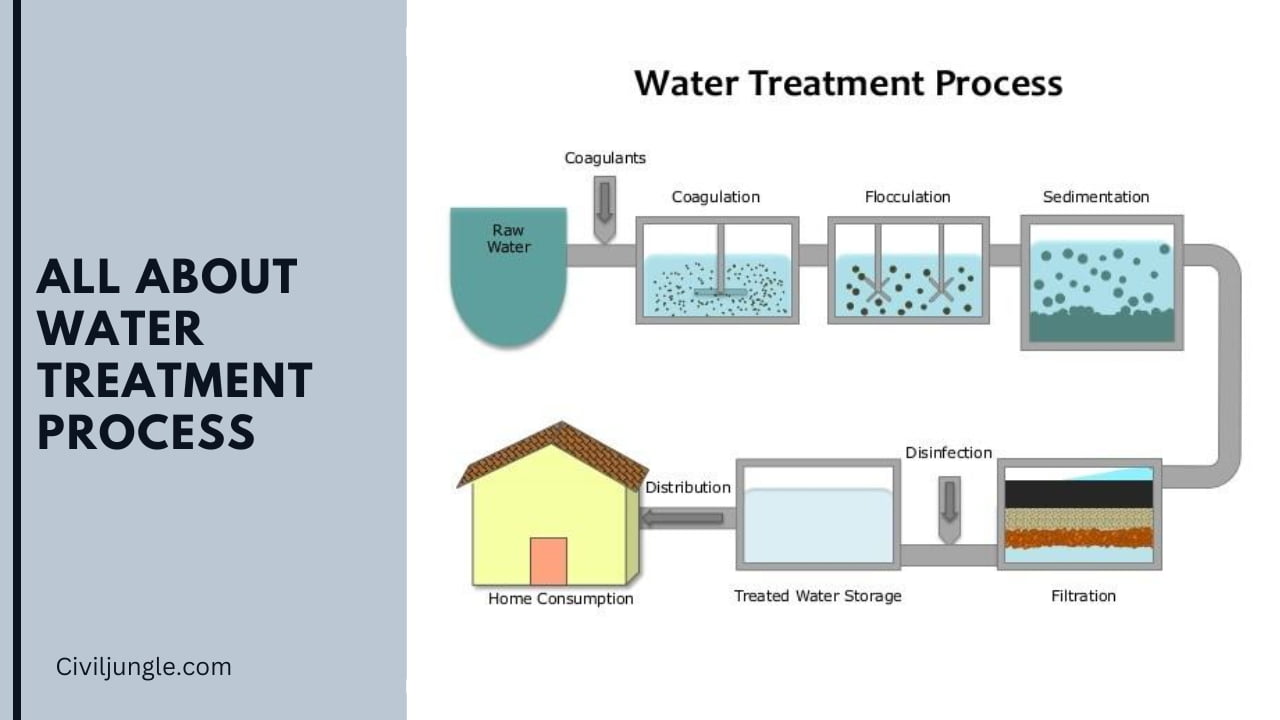
What Is Water Treatment Process?
Public water systems often use a series of water treatment steps that include coagulation, flocculation, sedimentation, filtration, and disinfection.
Water Treatment Process Steps
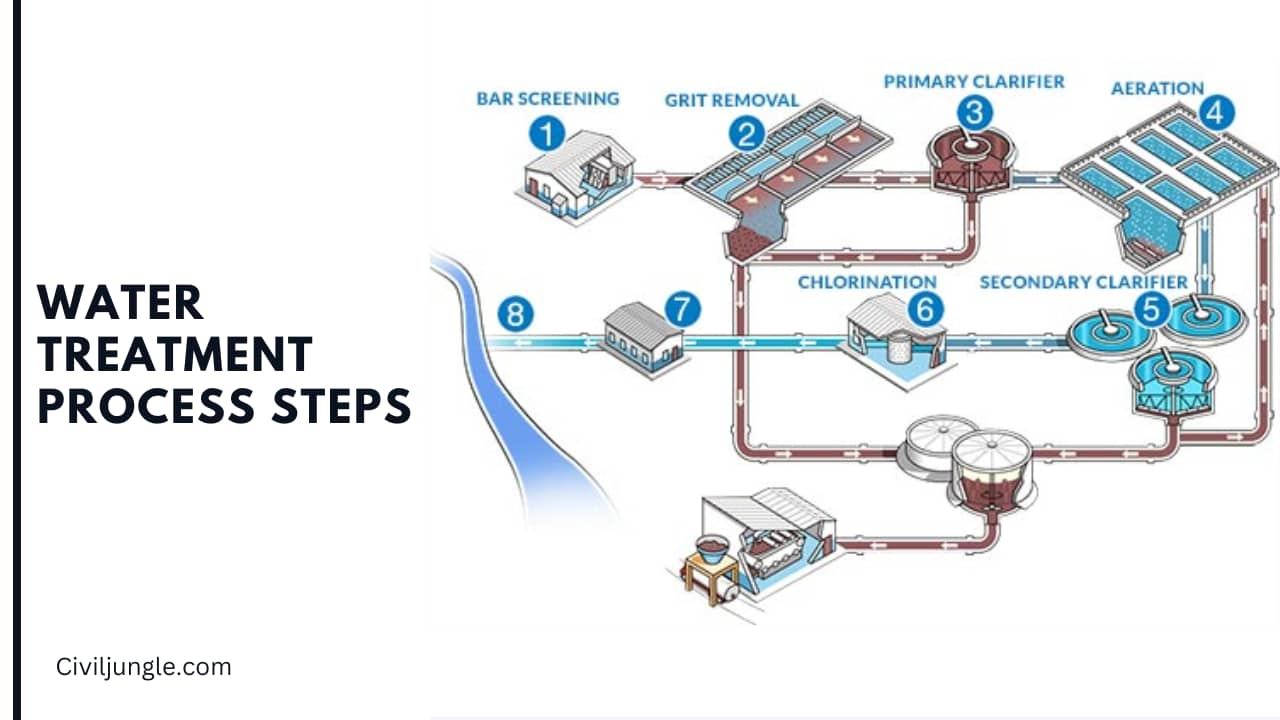
There are nine types of basic water treatment process steps that are described below-
1. Collection

Before treating water, firstly we have to collect the water from many sources like rivers, ponds, lakes, etc. But the collecting process of those waters is very difficult because they can be collected by complex pipelines and pumps, and that also can increase the total cost of the process.
2. Screening

When we are going to treat any type of water, we have to follow some steps, in those steps, screening is the first step that we have to follow.
In this screening process, we have to separate large particles or unusual materials from the water. This type of large material is removed by being captured with a large metal screen.
3. Chemical Addition

After that, this step will start, where chemicals are reacted with the smaller particles of the solution and create ‘floc.’ To initiate this process, some chemicals are used, which is known by coagulant. There are various types of coagulants are used in this process according to the situation and type of work.
4. Coagulation

In this step, we discuss about the working process of coagulants.
- Here, the coagulant is mixed with water, and after some time coagulant will start the coagulation process.
- The coagulation process is also known as flocculation.
After the completion of sedimentation, the water flows over the sedimentation basin. Some coagulated particles are stored at the bottom of the basin, and it will be removed after a certain period.
5. Filtration
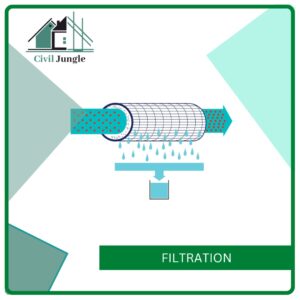
To filter the water more preciously, this step is done after the sedimentation process. Here, after sedimentation water is driven through different mediums like sand, activated granular carbons, gravel, etc to remove smaller particles.
6. Disinfection

After removing all the impurities from the water, there are also some amount of bacteria, microorganisms, viruses are present. To remove those particles, disinfection is necessary.
The most effective process to remove bacteria, microorganisms, and viruses is chlorination. It does not affect the taste of water, and there is no such higher chlorine odor.
7. Storage

After that, water is ready for service, but you need to store those water for future and emergency usage. Water is generally stored in underground tanks or over-ground tanks. Sometimes, drinking water are also stored for further usage.
8. Distribution
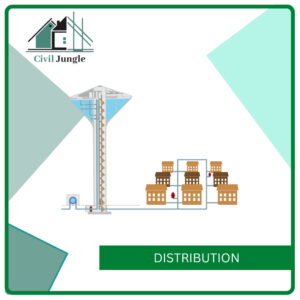
Finally, water is ready for distribution, and it is distributed through pipelines, pumps, hydrants, tankers, hydro-meter, etc.
- Drywall Water Damage Repair
- Top 10 Water Tank Brands in India
- What is Tremie Pipe | Tremie Method of Underwater Concrete
- All About Turbidity of Water | What Is Turbidity of Water | Procedure of Turbidity of Water Test
- Well Point System | Types of Well Point System | Well Point Dewatering | PVC Well Point | Well Point Installation | Well Point for Shallow Well
- All About Rainwater Harvesting | Purpose of Rainwater Harvesting | Methods of Rainwater Harvesting | Types of Rainwater Harvesting Tanks
Drinking Water Treatment
There are generally seven types of drinking water process is available, which are in following below-
1. Screening

- Screening is the process where it removes the major large floating and suspended particles.
- Generally, the water contains leaves, debris, paper, twigs, etc and those substances damage the equipment; that’s why the screening process is important.
- Two types of screen processes are available, those are coarse screen and fine screen.
- In coarse screen corrosion, resistive steel bars are placed at a distance of 5 to 15 cm. Here, screens are placed at 60 degrees.
- Fine screens are placed at just a lower level of the coarser screen. Here, steel bars are placed at a distance of 5 to 20 mm.
2. Aeration

- This step is done after the completion of the screening process; here, the aerated operation is done by absorbing oxygen from the air.
- The aeration process helps to remove some soluble gases like carbon dioxide, hydrogen sulfide, etc.
- Sometimes, iron and manganese are present in soluble form in the water. Aeration helps to remove those materials from that.
- Sometimes, a higher amount of algae is present in the water, and it blocks the sand filter. To overcome this situation chlorination process is done to remove. The main steps of water treatment come after this step.
3. Coagulation and Flocculation

- To remove the small particles and suspended particles, the process is done.
- In the coagulation tank, a high-speed impeller is rotated to mix the coagulant properly.
- Flocculation takes place after coagulation is completed.
- In this step, water is gently stirred, and flocs are getting connected with another floc and create larger flocs.
- In flocculation, water flows through the basin at a very low speed. Here, different chamber is present to create flocs.
3. Sedimentation
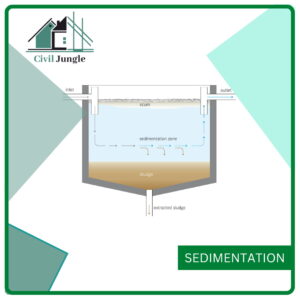
- After large flocs are obtained, then it settles at the bottom of the basin.
- Generally, for this operation, water is kept at the chamber for a long period.
- The materials which are stored at the bottom portion is called sludge, and there is a certain way to remove that material.
4. Filtration
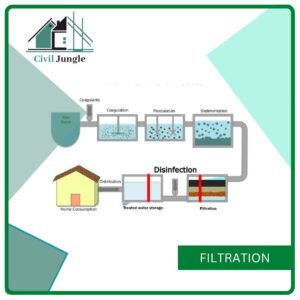
- This is the fifth step of water treatment process, where solids are separated from the water.
- In this step, the filter have a filtration rate of 4 to 5 cubic meter per square meter, and a rapid gravity technique also takes place.
5. Chlorination
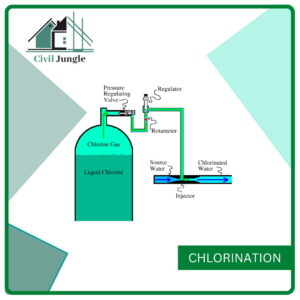
- This process is done to remove bacteria, microorganisms, etc.
- It is the most effective process because it is simple & cheap.
6. Supplementary Treatment
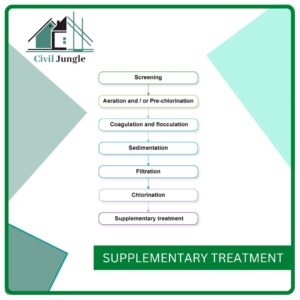
Sometimes supplementary treatments are applied by adding fluoride and the name of the process is fluorination.
Drinking Water Quality Standards

Different types of parameters are discussed below:-
| Sl. No. | Parameters | Drinking Water IS 10500: 2012 | |
| Permissible limit | Maximum limit | ||
| 1 | Odor | Agree | Agree |
| 2 | Taste | Agree | Agree |
| 3 | pH | 6.5 to 8.5 | No Relaxation |
| 4 | TDS (mg/l) | 500 | 2000 |
| 5 | Hardness (as CaCo3) (mg/l) | 200 | 800 |
| 6 | Alkalinity (as CaCO3) (mg/l) | 200 | 600 |
| 7 | Nitrate (mg/l) | 45 | No Relaxation |
| 8 | Sulfate (mg/l) | 200 | 400 |
| 9 | Fluoride (mg/l) | 1 | 1.5 |
| 10 | Chloride (mg/l) | 250 | 1000 |
| 11 | Turbidity (NTU) | 5 | 10 |
| 12 | Arsenic (mg/l) | 0.01 | 0.05 |
| 13 | Copper (mg/l) | 0.05 | 1.5 |
| 14 | Cadmium (mg/l) | 0.003 | No Relaxation |
What Are the Steps in Water Treatment Process?
They typically consist of several steps in the treatment process. These include: (1) Collection ; (2) Screening and Straining ; (3) Chemical Addition ; (4) Coagulation and Flocculation ; (5) Sedimentation and Clarification ; (6) Filtration ; (7) Disinfection ; (8) Storage ; (9) and finally Distribution.
What Are the 7 Methods of Water Treatment?
- Coagulation / Flocculation: Coagulation is adding liquid aluminum sulfate or alum and/or polymer to raw or untreated water. The resulting mixture causes the dirt particles in the water to coagulate or stick together.
- Sedimentation: When water and flocs undergo the treatment process, they go into sedimentation basins. Here, water moves slowly, making the heavy floc particles settle to the bottom.
- Filtration: In filtration, water passes through a filter, which is made to take away particles from the water. Such filters are composed of gravel and sand or sometimes crushed anthracite.
- Disinfection: Before water goes into the distribution system, it is disinfected to get rid of disease-causing bacteria, parasites and viruses. Chlorine is also applied since it is very effective.
- Sludge Drying: Solids that have been gathered and removed from water via sedimentation and filtration are transferred to drying lagoons.
- Fluoridation: Fluoridation treats water supplies of communities to adjust the concentration of free fluoride ions to an optimal level so that dental cavities can be reduced.
- pH Correction: To adjust pH levels, lime is combined with filtered water. This, also, stabilizes naturally soft water so corrosion can be minimized in the water distribution system and plumbing of customers.
What Are 3 Different Methods of Water Treatment?
When reverse osmosis is not available, there are 3 water purification methods that you can use to make your water safe for drinking.
- Boiling: Boiling water is the cheapest and safest method of water purification. Water sources and or channels of distribution may render your water unsafe.
- Filtration: Filtration is one of the effective ways of purifying water and when using the right multimedia filters it’s effective in ridding water of the compounds.
- Distillation: Distillation is a water purification method that utilizes heat to collect pure water in the form of vapor. This method is effective by the scientific fact that water has a lower boiling point than other contaminants and disease-causing elements found in water.
What Is Water Treatment and Why Is It Important?
Water treatment is a process involving different types of operations (physical, chemical, physicochemical and biological), the aim of which is to eliminate and/or reduce contamination or non-desirable characteristics of water. The objective of this process is to obtain water with the right features for the use intended for it. This is why the water treatment process varies as a function of the properties of the water being supplied and its final use.
Is Treated Water Safe to Drink?
Yes. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) limits the amount of chlorine in drinking water to levels that are safe for human consumption. The levels of chlorine used for drinking water disinfection are unlikely to cause long-term health effects.
What Is the Most Important Step in Drinking Water Treatment?
Filtration is necessary due to the small, dissolved particles that are still present in clear water, which include dust, parasites, chemicals, viruses, and bacteria. In filtration, water passes through physical particles that vary in size and composition.
What Are the Benefits of a Drinking Water Treatment Plant?
The water treatment plants remove the chemicals, particulates, organic materials as well as other debris from the water and treat the water resulting in clean and potable water that can be used for cooking, cleaning, etc.
Is Reverse Osmosis Water Good for You?
According to the World Health Organization, low mineral (TDS) drinking water produced by reverse osmosis or distillation is not suitable for long term human consumption and in fact, can create negative health effects to those consuming it. This lack of minerals may also impact the taste negatively for many people.
What Are the Problems with Water Treatment?
Training issues. Bacteria control. Poor monitoring and record keeping. Equipment design and specification.
Can You Drink Rain Water?
While useful for many things, rainwater is not as pure as you might think, so you cannot assume it is safe to drink. Rain can wash different types of contaminants into the water you collect (for example, bird poop on your roof could end up in your water barrel or tank).
How Do You Treat Lake Water for Drinking?
Boiling is the best way to kill disease-causing organisms, including viruses, bacteria, and parasites. The high temperature and time spent boiling are very important to effectively kill the organisms in the water. Boiling will also effectively treat water if it is still cloudy or murky.
What’s the Healthiest Way to Drink Water?
Why warm water may be better for your body.
- It can help cleanse the body by flushing out toxins.
- It can help break down food faster and keep the digestive system on track.
- It improves blood circulation, while cold water slows it down.
How Do You Purify Water in the Wild with Nothing?
Use UV lights or purification tablets to kill bacteria in their water supply and make it drinkable. Alternatively, use the sun’s ultraviolet (UV) rays to distill your water and eliminate pathogens.
How Do You Remove Chemicals from Water?
Distillation Systems will remove common chemical contaminants, including arsenic, barium, cadmium, chromium, lead, nitrate, sodium, sulfate, and many organic chemicals.
Is It Ok to Drink Reverse Osmosis Water?
There is virtually no tried-and-tested evidence to suggest that reverse osmosis water is harmful to your health. If you eat a balanced diet and do not suffer from conditions like severe acid reflux or gastrointestinal ulcers, drinking reverse osmosis water will have no impact on your overall health and wellbeing.
How Can You Make Drinking Water Safe?
Boil: If you don’t have safe bottled water, you should boil your water to make it safe to drink. Boiling is the surest method to kill disease-causing germs, including viruses, bacteria, and parasites. adding a pinch of salt for each quart or liter of boiled water.
Can You Filter Lake Water to Drink?
Because lake water can accumulate runoff, animal excretions, and pollution from boats and machinery, it is important to follow the proper filtration process before you do. Lake water is rarely drinkable, but with the proper filtration, you can have great tasting water.
Like this post? Share it with your friends!
Suggested Read –
- Best Concrete Mix for Driveway Repair
- All About Wood | Types of Wood | What Is Wood | Advantages of Wood
- All About of Corrosion | What Is Corrosion | 9 Different Types of Corrosion
- All About Tile Popping | What Is Tile Popping | Reason for Tile Popping | How to Fix Popped-Up Tiles
- All About Transportation of Concrete | What Is Transportation of Concrete | Methods for Transportation of Concrete
- All About Asphalt Flooring | What is Asphalt Flooring | Asphalt Flooring Used | Asphalt Flooring Advantages and Disadvantages
- All About Roof Overhangs | 10 Various Types of Roof overhangs | Standard Roof Overhangs | Overhang Roof Design | Roof overhangs on houses

