
What is Plumbing?

Plumbing may be a system that conveys fluids for a good range of operations. The plumbing system is used for water distribution systems. Plumbing systems use pipes, valves, plumbing fixtures, tanks, and other apparatuses to convey fluids.
Heating and cooling, waste junking, drinkable water delivery are among the foremost common uses for plumbing, but it’s not limited to those operations. The word derives from the Latin language for lead, plumbum, because the first effective pipes utilized in the Roman period were lead pipes.
Plumbing systems include domestic water (cold and hot), sanitary sewer, vent, storm drain, special waste like grease, and special systems (oxygen, fuel-gas, vacuum, nitrogen).
Plumbing Fixture

The plumbing system is the system of water carried under pressure. A plumbing fixture is an exchangeable device connected to plumbing to deliver and drain water.
This could include a plumbing fixtures list of items like pipes, washbasins, and more. The most common Plumbing fixtures are used in buildings.
Types of Plumbing Fixtures

List of Bathroom Fixture as follows.
- Pipes
- Hose Bib
- Tapware
- Terminal Valves
- Washbasins
- Water Closet
- Bidets
- Kitchen Sinks
- Bathtubs
- Showers
- Urinals
- Flush Cisterns
1. Pipes

Pipes are an example of plumbing fixtures provided for carrying water. This is just one plumbing fixtures example among many.
Several types of pipes are used for carrying the water in plumbing systems. Such as cast iron pipes, wrought iron pipes, steel pipes, concrete pipes, galvanized iron pipes, copper pipes, etc.
2. Hose Bib (Connections for Water Hoses)

Hose bibs are the Plumbing fixtures provided in the exterior of the house. Hose bibs are outdoor faucets that carry water from indoor systems outside.
3. Tapware

Tapware is the plumbing fixtures provided in an industry. The plumbing fixtures consist of tap valves, also called water taps or faucets, and their accessories, like water spouts and showerheads.
4. Terminal Valves

Terminal valves are the Plumbing fixtures provided in the pipeline to control water flow. Terminal valves are used for dishwashers, ice makers, humidifiers, etc.
5. Washbasins

Washbasins are the plumbing fixtures for washing hands and face and brushing teeth in a standing position. These are generally made of glazed earthenware or vitreous china. Occasionally these are also made of iron, stainless steel, or plastic.
6. Water Closet
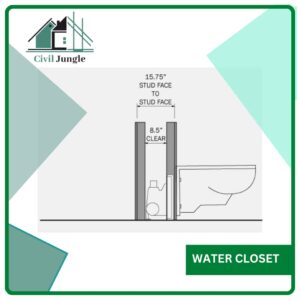
A water closet is a visage-like water flushed plumbing fixture designed to admit human excreta directly from the user. It is made of vitreous china or porcelain and is connected to the soil pipe utilizing a trap. The water closet’s inside face and the trap is made smooth by glazing to ensure an effective flush.
7. Bidets

A bidet is a plumbing fixture installed as a separate unit in the bathroom besides the toilet, shower, and sink.
8. Kitchen Sinks

Sinks are the plumbing fixtures handed in kitchens for cleaning utensils. For cleaning laboratory earthenware, Sinks are also provided in laboratories.
9. Bathtubs
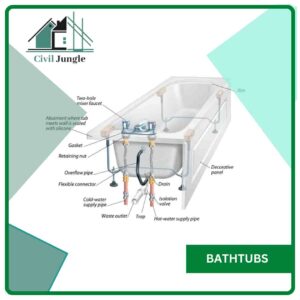
Bathtubs are the plumbing fixtures handed in the bathrooms for taking a bath. These are generally made of glazed earthenware cement concrete finished with terrazzo or glazed porcelain tiles or marble titles and enameled iron. For draining, the bathtubs are handed with an indirect waste hole at the bottom.
10. Showers

Showers are the Plumbing fixtures provided in the bathrooms.
11. Urinals

Urinals are the plumbing fixtures handed to urinate.
12. Flush Cisterns

Flushing cisterns are the plumbing fixtures for flushing out water closets and urinals. These are cast iron, glazed earthenware or vitreous china, or plastic.
Plumbing Fixture Units

Plumbing Fixture Units or Drain Fixture Units may be a unit of measure, based on the rate of discharge, operation time, and frequency of use of a fixture.
This helps in understanding what are plumbing fixtures and their impact on the plumbing system. This expresses the hydraulic cargo assessed by that fixture on the sanitary plumbing installation. A Fixture Unit isn’t an inflow unit but a design factor. Plumbing fixture units pipe sizing
Plumbing Fixture Units Pipe Sizing

With the sizing of a domestic water system and determining pipe sizes, it’s important to know the concept of fixture units, which can be found in a list of plumbing fixtures and fittings. Water Supply Fixture Units (WSFU) is the standard method for estimating the water demand for a building.
This system assigns an arbitrary value called a WSFU to every fixture during a building, supporting the quantity of water required and, therefore, the frequency of use.
The water system fixture units differ between cold, hot, or both. A plumbing line serves only the cold water side; then, the corresponding value should be used.
For example, a path may serve both cold and predicament; on the other hand, a spur track may attend the water heater. The spur track would only use the current water value.
It is extremely difficult to quickly obtain the speed, water demand, friction loss, and static pressure losses within a piping system to size the plumbing lines. Often, estimates are wont to size the most and branch piping, which may cause inaccuracies and increased pressure losses or oversized piping.
These estimates typically consist of a table of copper pipe sizes and, therefore, the maximum fixture units that every pipe size can serve.
The designer will sum the WSFUs served by each pipe then choose a pipe size that will accommodate the entire WSFUs. This process is strictly and equipment because of the previous process, with a table and the maximum WSFUs for every pipe size.
The table is often customized for any pipe material, tank, or flush valve and any range of velocities and pressure drops. The previous process determined the maximum WSFUs for a pipe size supported some random velocity and pressure loss limitations.
Still, advanced velocities are often accommodated in areas where bang and noise aren’t problems. Advanced pressure drops also can be accommodated on piping that’s not a part of the hydraulically remote run.
In both processes, the pipeline layout must be completed. The pipeline layout consists of a geometrical arrangement of the pipes from the water system to any plumbing fixtures.
Water Pipe Sizing

Water pipe sizing procedures are based on pressure requirements and losses. The appliances, appurtenances, and fixtures that will not reference within the table below shall be permitted to be sized about fixtures having an identical flow rate and frequency of use.
The listed fixture unit values mirror their load on the cold water building supply. The separate cold water and predicament water fixture unit value for fixtures having both hot and cold water connections shall be allowed to be each taken as three-quarters of the listed total value of the fixture.
For fixtures or supply connections likely to impose continuous flow demands, determine the required flow in gallons per minute (GPM or L/s). It is added separately to the demand in GPM (L/s) for the water distribution system.
Minimum fixture branch pipe size refers to the dimensions of the cold branch pipe. The minimum supply branch pipe sizes for individual fixtures are nominal (ID) pipe sizes.
Water Pipe Sizing Charts
| Appliances, Appurtenances, or Fixtures | Minimum Fixture Branch Pipe Size (inches) | Private | Public |
| Bathtub or Combination Bath/Shower | 1/2 | 4 | 4 |
| 3/4? Bathtub Fill Valve | 3/4 | 10 | 10 |
| Bidet | 1/2 | 1 | — |
| Clothes Washer | 1/2 | 4 | 4 |
| Dental Unit, Cuspidor | 1/2 | — | 1 |
| Dishwasher, Domestic | 1/2 | 1.5 | 1.5 |
| Drinking Fountain or Water Cooler | 1/2 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| Hose Bib | 1/2 | 2.5 | 2.5 |
| Hose Bib, Each Additional | 1/2 | 1 | 1 |
| Lavatory | 1/2 | 1 | 1 |
| Lawn Sprinkler, Each Head | — | 1 | 1 |
| Mobile Home, Each (minimum) | — | 12 | — |
| Bar Sink | 1/2 | 1 | 2 |
| Clinic Faucet Sink | 1/2 | — | 3 |
| Clinic Flush meter Valve Sink (with or without faucet) | 1 | — | 8 |
| Kitchen Sink, Domestic (with or without a dishwasher) | 1/2 | 1.5 | 1.5 |
| Laundry Sink | 1/2 | 1.5 | 1.5 |
| Service Sink or Mop Basin | 1/2 | 1.5 | 1.5 |
| Washup Sink (each of faucets) | 1/2 | — | 2 |
| Shower, Per Head | 1/2 | 2 | 2 |
| Urinal, Flush Tank | 1/2 | 2 | 2 |
| Wash Fountain (circular spray) | 3/4 | — | 4 |
| Water Closet, 1.6 GPF Gravity Tank | 1/2 | 2.5 | 2.5 |
| Water Closet, 1.6 GPF Flush meter Tank | 1/2 | 2.5 | 2.5 |
| Water Closet, Greater than 1.6 GPF Gravity Tank | 1/2 | 3 | 5.5 |
Conclusion of Water Pipe Sizing Charts
The most common Plumbing fixtures are used in buildings. Several plumbing fixtures are available in the markets, like basins, bathtubs, washbasins, kitchens sinks, flush cisterns, valves, pipes, etc. Plumbing fixtures are getting various types, shapes, and sizes available in the markets. Water pipe sizing Charts refer to water pipe sizing.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What Is Plumbing, and Why Is It Important?
Plumbing is a system used to convey fluids, such as water and waste, through pipes, valves, and fixtures for various operations, including heating, cooling, and waste disposal. It ensures the efficient distribution of potable water and the proper removal of wastewater, making it essential for sanitation and daily activities.
What Are Plumbing Fixtures?
Plumbing fixtures are devices connected to a plumbing system to deliver and drain water. Examples include sinks, toilets, showers, and faucets. They play a crucial role in facilitating daily water-related tasks.
What Types of Pipes Are Commonly Used in Plumbing Systems?
Common types of pipes used in plumbing systems include cast iron, copper, galvanized iron, PVC (polyvinyl chloride), and PEX (cross-linked polyethylene). Each type has its specific uses and advantages, such as durability, flexibility, and resistance to corrosion.
What Is the Purpose of a Hose Bib?
A hose bib, also known as an outdoor faucet, is installed on the exterior of a building. It provides a connection point for water hoses, allowing for outdoor watering and other water needs.
How Do Tapware and Terminal Valves Function in Plumbing?
Tapware, including faucets and showerheads, controls the flow and temperature of water in fixtures. Te
rminal valves are used to control water flow to specific appliances or fixtures, such as dishwashers or ice makers, by regulating or shutting off water supply.
What Is the Difference Between a Washbasin and a Water Closet?
A washbasin is used for washing hands, face, and brushing teeth, typically found in bathrooms and made from materials like vitreous china. A water closet, commonly known as a toilet, is a plumbing fixture designed for flushing human waste and is usually made of vitreous china or porcelain.
How Are Kitchen Sinks and Bathtubs Different in Terms of Plumbing?
Kitchen sinks are used for cleaning dishes and food preparation, while bathtubs are designed for bathing. Both fixtures require plumbing connections for water supply and drainage, but bathtubs often have more complex drainage systems due to their larger volume.
What Are Flush Cisterns, and How Do They Work?
Flush cisterns are plumbing fixtures used to flush water closets and urinals. They store water and release it in a controlled manner to clear waste from the toilet or urinal bowl.
How Is Pipe Sizing Determined in Plumbing Systems?
Pipe sizing is determined based on factors like water demand, pressure requirements, and flow rates. Plumbing Fixture Units (PFUs) or Water Supply Fixture Units (WSFUs) are used to estimate the water demand for a building and help in selecting the appropriate pipe sizes.
Why Is Accurate Pipe Sizing Important?
Accurate pipe sizing ensures efficient water flow, minimizes pressure loss, and prevents issues such as water hammer or noisy pipes. It also helps in avoiding oversized or undersized pipes, which can lead to increased costs or system inefficiencies.
What Is the Role of Plumbing Fixture Units in Design?
Plumbing Fixture Units (PFUs) measure the hydraulic load a fixture imposes on the plumbing system. They help in designing and sizing plumbing systems to ensure that pipes can handle the expected water flow and pressure.
How Can I Find the Right Size for a Plumbing Pipe?
To find the right pipe size, refer to water pipe sizing charts that indicate minimum branch pipe sizes based on fixture type and usage. These charts provide guidance on selecting pipe sizes to meet the water demand and pressure requirements of various fixtures.

