
Top-Down Construction
The easy description of the top-down construction method will help the storeroom surface of the house will install in a system which, after realization of the cellar, will be set up from upper to lower surface by surface.
What Is a Top-Down Construction?
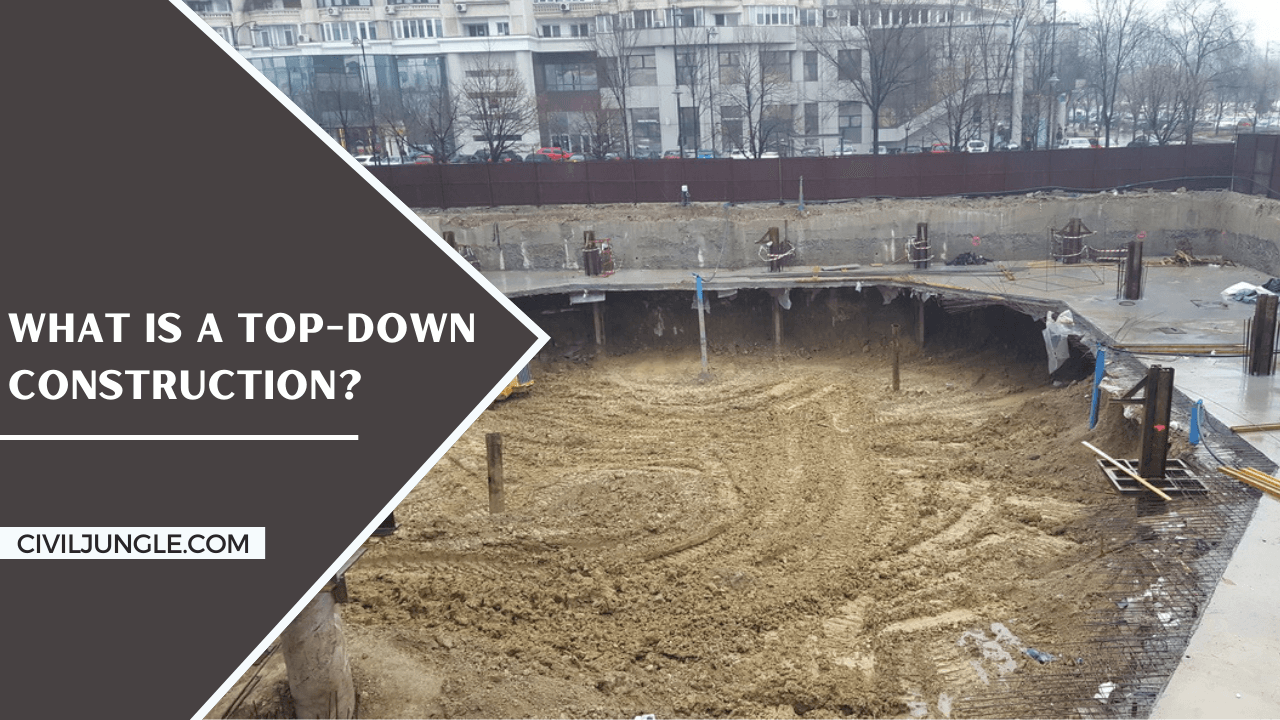
Regular houses with below-ground storage rooms will make by a backward process. But it is not possible for the massive design with little building time and other area obstructions.
The vertical building process allows the construction and store room to fix simultaneously. This process can decrease build time seriously.
Procedure of Top-Down Construction
Here, the steps procedure of top-down construction are as follows.
- Design of midriff wall.
- Construct wall fastener piles.
- It is a ditch of soil below a storeroom.
- Offer basic sweep to help midriff wall.
- Sling the surface slab of the following storeroom extent guide the next level of removal.
- Renew the equal method up to the wanted deepness will arrive.
- Install the base slab and basement beam.
- Continue installation of the construction until it reaches a goal.
Advantages of Top-Down Construction

Here, the pros of top-down construction are as follows.
- The infrastructure and construction can design in a comparable proposal.
- There is the fewest distraction at all to the nearby construction.
- You don’t have to think about the basement water.
- The design will finish firster.
- No huge work platform, and the channel helps will be necessary.
- Due to limited channels, the issue of mess will finish bypass.
Disadvantages of Top-Down Construction

Here, the cons of top-down construction are as follows.
- Powerlessness to design outward water-resistance outer surface of the wall.
- Hidden water discharge at the junction.
- It is more problematic joints for the surface, terrace, and foundation slabs.
- The approach to the area will be the bound and bounded area for the basement building
- The compound plan is intricate.
Top-Down Construction Method
Top-down will describe the process of the fixed indoor design as the short-term bore to the containing wall heaved in top-down order. The top-stage slabs are thrown before the bottom-stage slabs to work as a parallel framework for wall help as the revealing boost.
The top-down method primarily applies to two kinds of inner-city buildings, large construction with depth underground and storeroom construction like the garage, crossroad, and tunnel position.
The method will apply to a depth-revealing design where the anchor blueprint was impossible and soil motion depreciated. There is a feasible of saving installation time.
The design starts with the breast wall construction and then supporting objects which conduct the upcoming building. These supporting objects will naturally cement piles.
FAQ on Top-Down Construction
What Is Top-Down Construction?
Top-down construction is a vertical building process where construction and below-ground storage rooms are fixed simultaneously. This method allows for building the structure from the top down, significantly reducing build time and accommodating area obstructions.
How Does Top-Down Construction Differ from Traditional Methods?
Unlike traditional methods that build from the bottom up, top-down construction starts with the surface level and works downwards. This is particularly useful for large designs with limited building time and space constraints.
What Are the Steps Involved in the Top-Down Construction Process?
The steps involved in top-down construction include:
- Designing the midriff wall
- Constructing wall fastener piles
- Excavating soil below the storeroom
- Offering basic support for the midriff wall
- Slinging the surface slab of the next storeroom level and guiding the next level of excavation
- Repeating the process until the desired depth is reached
- Installing the base slab and basement beam
- Continuing installation until the construction reaches its goal
What Are the Advantages of Top-Down Construction?
The advantages of top-down construction include:
- Simultaneous design and construction of infrastructure
- Minimal disruption to nearby structures
- No concerns about basement water
- Faster completion of the design
- No need for a large work platform or extensive shoring
- Reduced issues with mess due to limited channels
What Are the Disadvantages of Top-Down Construction?
The disadvantages of top-down construction include:
- Inability to design outward water-resistant outer surfaces for walls
- Potential hidden water discharge at joints
- More complex joints for surface, terrace, and foundation slabs
- Limited access to the area, creating a bounded space for basement building
- Intricate compound planning
Where Is the Top-Down Construction Method Typically Used?
The top-down construction method is primarily used in two kinds of inner-city buildings: large constructions with deep underground levels and storage room constructions like garages, crossroads, and tunnel positions.
What Are the Key Considerations for Using the Top-Down Construction Method?
Key considerations for using the top-down construction method include:
- The feasibility of anchor blueprints and minimizing soil motion
- Saving installation time by starting with breast wall construction and supporting objects, which guide the subsequent building stages
- Typically utilizing cement piles for supporting objects
Is Top-Down Construction Suitable for All Types of Buildings?
Top-down construction is particularly suitable for large buildings with deep underground levels and projects with significant space constraints. It may not be ideal for all types of buildings, especially those requiring simpler or less intricate planning and execution.
How Does Top-Down Construction Handle Water Resistance?
One challenge of top-down construction is ensuring water resistance for outward walls. This can be managed by careful planning and incorporating water-resistant materials and techniques during the construction process.
What Are the Long-Term Benefits of Using Top-Down Construction?
The long-term benefits of using top-down construction include faster project completion, reduced disruption to surrounding areas, and efficient use of space and resources in urban environments.

