
What Is Coarse Aggregate?

There are many building materials which are used in the construction industry. Coarse Aggregate is one of the most important and massively used building material in the Construction Industry.
Aggregate is one of the most important component parts of the concrete. Coarse Aggregates gives volume to the Concrete. Coarse Aggregates in concrete provides body and strength to the concrete and acts as a filler material which will give the homogeneous mass of the concrete.
Coarse aggregates are used in every Construction projects which includes the construction of roads, Buildings, Railway Tracks etc.
Coarse Aggregate in concrete was considered as chemically inactive and acts as a filler material only. The coarse aggregates are used for the manufacturing of mortar and concrete.
In this article, you will get to know all about coarse aggregates, classification of coarse aggregate, properties of the coarse aggregates and the different tests which are performed on the Coarse Aggregates.
Coarse Aggregate Definition-

The Aggregates which will get retained on the 4.75 mm sieve or the aggregates which have size more than 4.75 mm are known as Coarse aggregate.
Origin of Aggregates-
Aggregates are commonly obtained by crushing the naturally occurring rocks. The properties of the rocks are mainly depended upon the type of rock whether it is sedimentary rocks, igneous rock or metamorphic rocks.
Requirements of Good Coarse Aggregates:

The Aggregates which are used in the construction must have the following properties
- The coarse aggregate should be durable.
- The coarse aggregate should be hard and strong.
- It should be clean and free from the dust and organic materials otherwise it will reduce the bonding of the aggregate with concrete.
- The aggregates should not react with the cement after mixing.
- Coarse aggregates should not be soft and porous.
- Coarse Aggregates should not absorb water by more than 5%.
- Aggregates should be chemically inert.
- The shape is of the aggregate preferably cubical or spherical.
Requirements of Good Coarse Aggregates:
- It should be angular or cubical in shape.
- It must be sound & durable.
- A Good Coarse Aggregate should be absolutely clean and free from any organic matter, chemicals and coating of clay.
- It should be hard and tough.
Uses of Coarse Aggregates in the Construction Works:

The coarse aggregates have many advantages which are listed are as follows
- In the construction of railway tracks, coarse aggregates are widely used in the railway ballast which will help to uniformly distribute the load.
- It will help to increase the volume of the concrete and also reduces the cost of the project.
- Coarse aggregates are also used in the construction of Roads.
- The Coarse Aggregates are also used as the upper layer on the rainwater harvesting to drain off the water into the ground.
Uses of Coarse Aggregates-
Coarse aggregates are irregular broken stone or naturally-occurring rounded gravel used for making concrete. For non-structural mass concrete of low strength, broken bricks, foamed slag, clinker, etc., may be also used as coarse aggregates.
[/su_box]Classification of the Aggregates:

The coarse Aggregates are mainly classified are as follows.
- According to the source or the nature of the formation of the aggregate.
- According to the size of the aggregate
- According to the shape of the aggregate
The description of the classification of the Aggregates are as follows.
Classification According to the Source or Nature of Formation

- Naturally Occurring Aggregates.
- Artificially Manufactured Aggregates.
#1 Naturally Occurring Aggregates-
Coarse Aggregates are obtained from the stone quarries and the stone crushers. Natural aggregate materials originate from bedrocks.
#2 Artificially Manufactured Aggregates-
The broken bricks or blast furnace slag are the artificial aggregates which are also used for the various concreting work. The Air-cooled slag is also used as a coarse aggregate as well as fine aggregates. It has fire resistance Property.
Classification of Aggregates According to the Size

Aggregate Types:
The Aggregates are mainly classified into two types which are given below:
- Fine Aggregates
- Coarse Aggregates
#1 Fine Aggregates-
The Aggregates which has a size less than 4.75 mm is known as fine aggregate.
#2 Coarse Aggregates-
The Aggregates which has a size of more than 4.75 mm is known as Coarse aggregate. The Aggregate sizes which range from 4.75 mm to 80 mm are the coarse Aggregates and the 150 microns to 4.75 mm aggregates are known as Fine Aggregates.
The size 4.75 mm is common for both fine Aggregates as well as coarse Aggregates.
Classification According to the Shape of the Aggregates

- Rounded Aggregates.
- Angular Aggregates.
- Flaky Aggregates.
- Irregular Aggregates.
The Irregular and angular aggregates give greater bond strength as compared to the rounded and flaky Aggregates due to their shape because there is more interlocking effect in this Aggregates.
#1 Rounded Aggregates-
Natural aggregates smoothed by weathering, erosion and attrition. Rocks, stone, sand and gravel found in riverbeds are your most common rounded aggregates. Rounded aggregates are the main factor behind workability.
#2 Angular Aggregates-
Angular aggregates have a higher specific surface area than the smooth rounded aggregate. With a greater specific surface area, the angular aggregate may show higher bond strength than rounded aggregates.
Also, angular aggregates exhibit a better interlocking effect in concrete that contributes to the strength of concrete.
#3 Flaky Aggregates-
an aggregate is termed flaky when its least dimension (thickness) is less than three-fifths of its mean dimension. The mean dimension of aggregate is the average of the sieve sizes through which the particles pass and are required, respectively.
#4 Irregular Aggregates-
These are also shaped by attrition but are not fully rounded. These consist of small stones and gravel and offer reduced workability to rounded aggregates.
Properties of Coarse Aggregates

The coarse aggregates are widely used in the construction so it is very important that we should know about the properties of the Coarse Aggregates. The properties of the coarse aggregates are as follows:
- Size.
- Shape.
- Surface Texture.
- Water Absorption.
- Soundness.
- Specific Gravity.
- Bulk Density.
#1 Size-
The size of the coarse aggregate depends upon the purpose for which the concrete is used in the construction. For the mass concreting work the larger aggregates of 80 mm,40 mm and 20 mm sizes are used. For the construction of residential building generally, 20 mm size aggregate is used.
#2 Shape-
The Shape of the aggregate is one of the most important factors which affects the workability of Concrete. The shape of the Aggregates also affects the bonding strength.
Generally, the angular and Irregular shape of aggregates is used because they have more Interlocking effect. The total surface area of the angular aggregate is more in the angular aggregates as compared to the rounded Aggregates.
#3 Surface Texture-
The surface texture of the aggregate deals with the roughness and the smoothness of the coarse aggregates.
The coarse aggregate with rough texture is preferred because it forms a good bond with the concrete and gives more bonding strength. But the Rough textured aggregate will give less workability.
The surface texture of the rounded aggregate with a smooth surface will require less amount of cement paste and hence increased the yield per bag.
#4 Water Absorption-
Water absorption is one of the most important properties of the coarse aggregate which is measured in the percentage. If the aggregate absorbs water then the water contained in the concrete will get increased and the concrete will require higher water cement ratio.
Water absorption of the coarse aggregate depends upon the porosity of the aggregate. If the water absorption is more then it will affect the workability and the durability of the concrete.
#5 Soundness-
The soundness of the aggregate is defined as the resistance which is offered by the aggregates to any type of volume change.
Porous aggregates are unsound and more liable to the attacks by the chemicals. The foundation of the aggregates is measured by putting the aggregates in the sodium or magnesium sulphate and then oven drying it.
#6 Specific Gravity-
Specific gravity is defined as the ratio of the dry weight of the aggregate to the weight of an equal volume of water.
The specific gravity of the aggregate is the indication of the Strength. Generally, the aggregates with the specific gravity range from 2.5 to 3.0 are used in the construction work. Greater the specific gravity more will be the strength.
#7 Bulk Density-
The bulk density of the aggregate defined as the ratio of the net weight of the aggregate to the volume of the aggregate.
Grading of Coarse Aggregate:
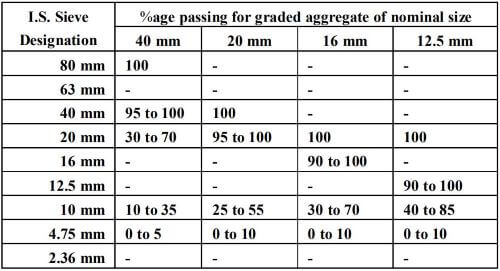
The grading of coarse aggregate for coarse material is the art of doing particle size distribution of the aggregate. The grading of the coarse aggregate affects the workability, strength and durability of the concrete which is used in the construction.
It is very necessary to do the proper grading of the aggregates in order to make the structure dense and prevent the problem of honeycombing. Grading of aggregate is done to achieve proper finishing and workability of the concrete.
Different Types of Test Which Are Carried Out on the Coarse Aggregates

#1 Crushing value of Aggregate ( IS 2386 Part IV -1963)
The crushing value of the coarse aggregate is defined as the relative measure of the resistance which is offered by the aggregate to the crushing under the gradually applied load.
#2 Impact value of Aggregate ( IS 2386 Part IV -1963)
Impact value of the coarse aggregate is the test which gives a relative measure of the resistance offered by the aggregate to the suddenly applied load which is also known as impact load.
#3 Abrasion Value Test ( IS 2386 Part IV -1963)
Abrasion value test of the coarse aggregate will give the relative resistance of the aggregate to the wearing. Abrasion value of the coarse aggregate help to know whether the aggregates are suitable to use for wearing surfaces.
#4 Flakiness Index of coarse Aggregates ( IS 2386 Part I -1963)
The flakiness index of the aggregate is the percentage by the weight of the particles whose least dimension or the thickness is less than 3/5th of their mean dimension. The flakiness index of the aggregate will give the idea about the thickness of the aggregate.
#5 Elongation Index of Coarse Aggregate ( IS 2386 Part I -1963)
The elongation index of the aggregate is the percentage by the weight of the particles whose greatest dimension or the length is greater than 1.8 times of their mean dimensions.
FAQ: Coarse Aggregates
What Are Coarse Aggregates?
Coarse aggregates are materials with a size greater than 4.75 mm, used primarily in concrete and construction. They provide bulk, strength, and stability to the concrete mix.
What Are the Main Types of Coarse Aggregates?
Coarse aggregates are classified based on their source (naturally occurring or artificially manufactured), size (ranging from 4.75 mm to 80 mm), and shape (rounded, angular, flaky, or irregular).
How Are Coarse Aggregates Sourced?
Coarse aggregates are commonly obtained by crushing naturally occurring rocks, such as granite, basalt, or limestone. They can also be manufactured from materials like broken bricks or blast furnace slag.
What Properties Should Good Coarse Aggregates Have?
Good coarse aggregates should be durable, hard, clean, chemically inert, and not absorb more than 5% water. They should ideally have an angular or cubical shape for better bonding and strength.
What Is the Importance of Coarse Aggregate Size in Construction?
The size of coarse aggregates affects the workability and strength of concrete. Larger aggregates are typically used for mass concrete works, while smaller aggregates are preferred for residential construction to improve workability.
How Does the Shape of Coarse Aggregates Impact Concrete Quality?
Angular and irregular-shaped aggregates offer better interlocking and bond strength compared to rounded or flaky aggregates. This enhances the overall strength and stability of the concrete.
What Are the Common Tests Performed on Coarse Aggregates?
Common tests include:
- Crushing Value Test: Measures resistance to crushing under load.
- Impact Value Test: Assesses resistance to sudden impacts.
- Abrasion Value Test: Determines resistance to wear and tear.
- Flakiness Index: Evaluates the thickness of the particles.
- Elongation Index: Measures the length of the particles compared to their mean dimension.
Why Is Water Absorption of Coarse Aggregates Important?
Water absorption indicates the porosity of the aggregates. High water absorption can lead to increased water content in the concrete mix, affecting workability and durability.
How Does Grading of Coarse Aggregates Affect Concrete?
Proper grading ensures a well-distributed particle size, which enhances workability, reduces honeycombing, and improves the overall quality and strength of the concrete.
What Is the Role of Coarse Aggregates in Road Construction?
In road construction, coarse aggregates are used in the road base and sub-base layers to provide structural support, distribute loads, and improve durability.

