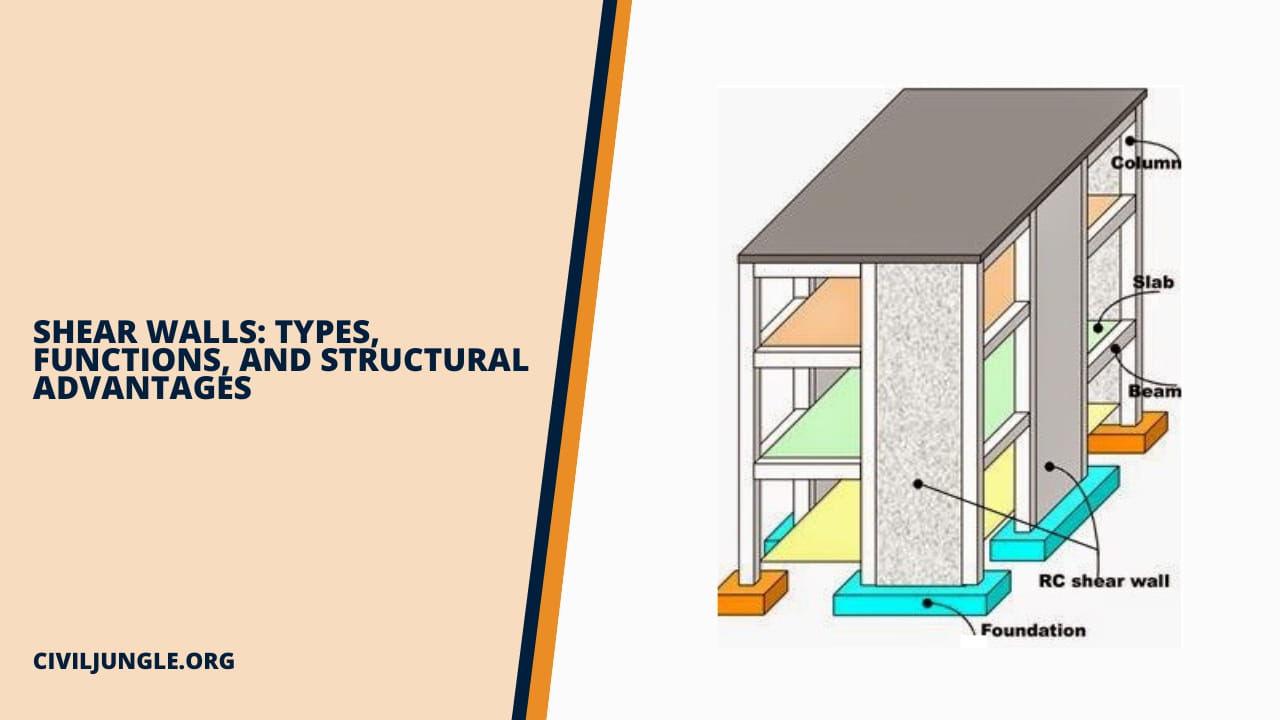
What is a Shear Wall?
Shear wall is a structural member used to resist lateral forces, i.e., parallel to the plane of the wall. In other words, Shear walls are vertical elements of the horizontal force resisting system. Shear wall is a structural member in a reinforced concrete framed structure to resist lateral forces such as wind forces.
This is rarely practical since it also utilizes the space a lot, so they are positioned at the ends. It is better to use walls with no openings in them. So, usually, the walls around lift shafts and stairwells are used.
Classification of Shear Walls:
1. Column Supported Shear walls.

2. Core Type Shear Walls.

3. Rigid Frame Shear Walls.

4. Framed Walls with Infilled Frames.

5. Simple Rectangular Types and Flanged Walls.

6. Coupled Shear Walls.

7. Cantilever Shear Wall

Types of Shear Wall:
Here, the different types of shear wall are as follows.
- Concrete Shear Wall
- Steel Plate Shear Wall
- Plywood Shear Wall
- RHCBM (RC Hollow Concrete Wall Masonry.)
Functions of Shear Wall:
The main functions of a Shear Wall can be described as follows :
- Strength to a building :
- Stiffness to a building :
1. Strength to a building
Shear Wall must provide lateral shear strength to the building to resist the horizontal earthquake forces, wind forces, and transfer these forces to the foundation.
2. Stiffness to a building
Shear Walls provide large stiffness to building in the direction of their orientation, which reduces the lateral sway of the building and thus reduces damage to the structure.
Purpose of Shear Wall:
Here, the purpose of shear wall are as follows.
- The verticle or gravity loads on the structure.
- The counter shear and uplift forces.
- The lateral loads of earthquakes and wind.
- To make the structure more stable.
Advantages of Shear Wall
Here, the pr0s of shear wall are as follows.
- These walls provide more strength, stability, and stiffness to a building.
- Reduce lateral sway of a building.
- Easy to construct and easily implemented at the site.
- Thinner walls, hence lightweight.
- Effective in minimizing earthquake damage in structural and non-structural elements.
Disadvantages of Shear Wall
Here, the cons of shear wall are as follows.
- Shear walls are difficult to construct.
- They have a flimsy appearance.
- Also, loud banging sounds associated with the buckling of web plates.
- It has low stiffness and energy dissipation capacity.
- Also, requires large moment connections.
Frequently Asked Questions (Faqs) You Could Include in Your Article About Shear Walls:
What Is a Shear Wall and How Does It Work in Building Structures?
Explain the basic concept of shear walls and their role in resisting lateral forces such as wind and earthquakes.
What Are the Different Types of Shear Walls?
Describe various types like concrete shear walls, steel plate shear walls, plywood shear walls, etc., highlighting their materials and applications.
How Do Shear Walls Contribute to the Overall Strength and Stability of a Building?
Discuss how shear walls enhance the structural integrity by providing strength against horizontal forces and reducing sway.
Where Are Shear Walls Typically Located Within a Building?
Explain the ideal placement of shear walls, often around lift shafts, stairwells, and at building corners to maximize their effectiveness.
What Are the Advantages of Using Shear Walls in Construction?
List benefits such as increased strength, reduced lateral movement, ease of construction, and enhanced earthquake resistance.
What Are the Challenges or Disadvantages Associated with Shear Walls?
Address issues like construction complexity, potential aesthetic concerns, and specific maintenance requirements.
How Are Shear Walls Designed and Engineered?
Provide insights into the design considerations, including thickness, reinforcement, and connection details to ensure optimal performance.
What Is the Difference Between Shear Walls and Other Lateral Load-Resisting Systems Like Moment Frames or Braced Frames?
Highlight the distinctive features and applications of shear walls compared to alternative structural systems.
What Are the Seismic Design Considerations for Shear Walls?
Discuss the importance of seismic design parameters, including ductility, detailing requirements, and performance during earthquakes.
How Can Shear Walls Be Retrofitted or Reinforced in Existing Buildings?
Offer strategies for retrofitting older structures with shear walls to enhance their resilience against seismic events and other lateral forces.
Advantages of Shear Wall
- These walls provide large strength and stiffness in the direction of orientation.
- Considerably reduces the lateral sway.
- They are easy in construction and implementation.
- It is efficient in terms of construction cost and effectiveness in minimizing earthquake damage.
Types of Shear Walls
- Reinforced Concrete Shear Wall.
- Concrete Block Shear Wall.
- Steel Shear Wall.
- Plywood Shear Wall.
- Mid-Ply Shear Wall.
Like this post? Share it with your friends!
Suggested Read –
- What Is Building Bye-Laws
- How to Building Construction Process Step by Step
- Difference Between CPM and PERT | What Is CPM & PERT
- Difference Between One Way Slab and Two Way Slab | What is Slab
- What Is Superstructures | Difference Between Load-Bearing and Framed Structures
- What Is Drip Irrigation| Drip Irrigation Advantages | Types of Irrigation | Drip Irrigation System





